YARD is an open-source web application for reviewing and enhancing research outputs.
YARD for Data Managers
Why use YARD?
YARD helps data archives and repositories manage their curation and review workflow and enables open access to data resources that have been fully reviewed and enhanced for long term usability and analysis.
YARD enables data managers to leverage the DDI standard for data documentation and structure the curation workflow.
YARD makes it easy for data managers and curators to replicate analyses and validate published results for each study before publishing the files online.
YARD generates high quality data packages that are repository-agnostic (i.e., they can be ingested into any repository).
YARD connects researchers, curators, and publishers through a single pipeline for the purpose of improving research transparency, reproducibility, and long-term use.
YARD combines several open source off-the-shelf components with a new, web-based data pipeline application, and enables a seamless framework for collecting, processing, archiving, and publishing data.
YARD roles:
- Depositors use the web application to upload files and provide basic information about their research by creating a catalog record.
- Curators are assigned to a catalog record. The curator is responsible for reviewing the record and all files. This review may include several checks, which are assisted by the software, such as:
- Finding and removing confidential or identifiable information
- Finding missing labels in data files and adding appropriate metadata
- Identifying potential data errors
- Confirming reported observation counts against the data
- Confirming that source code successfully builds and executes
- Confirming that source code replicates reported results
- Approvers or Admins can assign curators to records and approve publication.
How does YARD work?
The short version:
YARD structures and streamlines the curation and review process and generates high quality data packages.
YARD structures and records all curation and review actions, integrates and captures DDI metadata production with curation and review, and directs processed data packages to pre-specified destinations for publication.
YARD…
* Helps manage data curation and code review workflows.
* Integrates data curation and code review with metadata production.
* Tracks changes to files and metadata.
* Creates preservation metadata and file formats.
The longer version:
Upon deposit, a safe copy is created and deposited in a dark archive. A public copy of the files is created and begins processing, which includes generating study-level and file-level metadata, confirming all variables and values are labeled, standardizing missing values, creating and augmenting documentation, and assessing and minimizing disclosure risk by applying techniques such as recoding, masking, or removal of variables, and assigning persistent links. The review of code files—statistical and other programming scripts—includes verifying that the code executes and that the published scientific results can be reproduced with the given code and data. The data and code review processes include an assessment of the quality of documentation and contextual information necessary for long-term usability (for example: a codebook, a README file, or commented code). In cases where these are found lacking or insufficient, the archive works with researchers on remedial actions. All file formats are normalized (including migrating software-specific data files to flat file formats such as ASCII, text, or comma delimited, and rewriting code written using licensed statistical software such as SPSS to open-source statistical languages such as R). 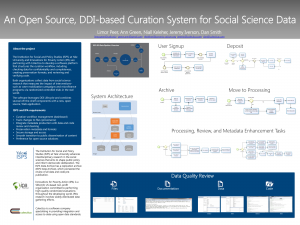 Once curation is complete and a catalog record is approved for publication, the system automatically performs several actions to aid in preservation and publication: Creates preservation formats for proprietary data files, requests persistent identifiers from the configured Handle service and stores them with the metadata, creates checksums for each file and stores them with the metadata, creates DDI metadata for all files and the catalog record itself, creates an archive package and places it in the configured archival location, and marks the catalog record as published. After completion of the process, materials are stored and made publicly available via a pre-specified destination.
Once curation is complete and a catalog record is approved for publication, the system automatically performs several actions to aid in preservation and publication: Creates preservation formats for proprietary data files, requests persistent identifiers from the configured Handle service and stores them with the metadata, creates checksums for each file and stores them with the metadata, creates DDI metadata for all files and the catalog record itself, creates an archive package and places it in the configured archival location, and marks the catalog record as published. After completion of the process, materials are stored and made publicly available via a pre-specified destination.
Click on the link below for background on the YARD project.
Interested in using YARD?
YARD can support multiple organizations with separate instances administered independently. A YARD “instance” is an organization-specific configuration of the software.
Are you at Yale University?
Organizations that provide access to research outputs can make decisions about storage location, roles and permissions, terms of use, and more.
At Yale, the tool as currently configured is feeding into the Institution for Social and Policy Studies’ ISPS Data Archive and intended for the use of ISPS affiliates.
Click on the link below to learn about how YARD is used at ISPS.
If you are not a member of the Yale community
You can still try YARD using our Sandbox environment. Experience YARD from a researchers’ point of view: describe and deposit research data via YARD.
Interested in exploring YARD as a curator? Email digitalscholarship.service@yale.edu to request curatorial access to the Sandbox.